Overview
GPU Virtual Machines (VMs) are Linux-based virtual machines that run on top of virtualized hardware with high-end GPUs. Each VM you create is a new virtual server that you can use either standalone or as part of a larger, cloud-based infrastructure.
Step 1: Open Instance Management
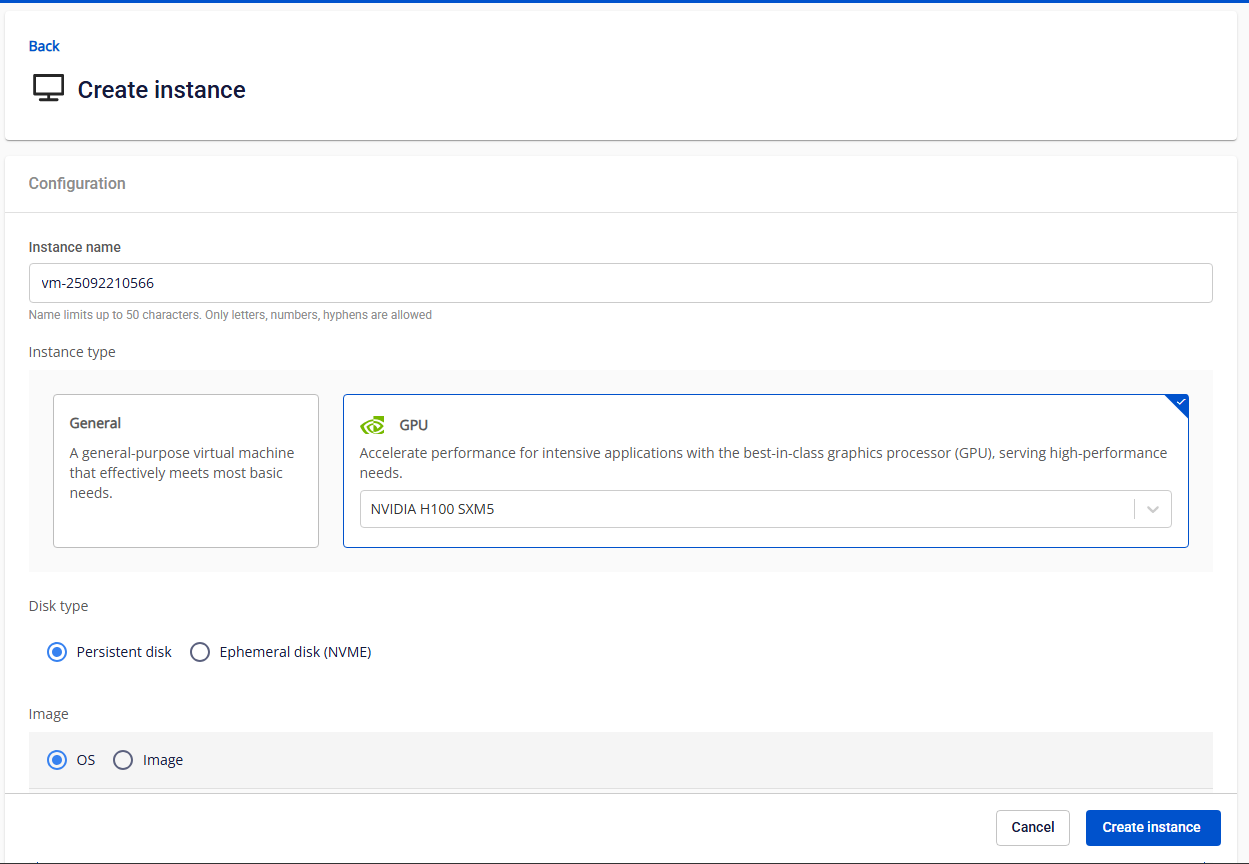
In the side menu, go to Compute Engine > Instance Management, then click Create Instance.
Step 2: Configure the Instance
-
Instance Name: Enter a unique name for your GPU virtual machine.
-
Instance Type: Select the type of instance. GPU: Optimized for high-performance computing, machine learning, and other intensive tasks.
Currently supported GPUs: NVIDIA H100 SXM5 and NVIDIA H200 SXM.
-
Disk Type: Only one disk type can be selected during GPU VM creation: Ephemeral Disk (NVMe) or Persistent Disk (Block Storage)
-
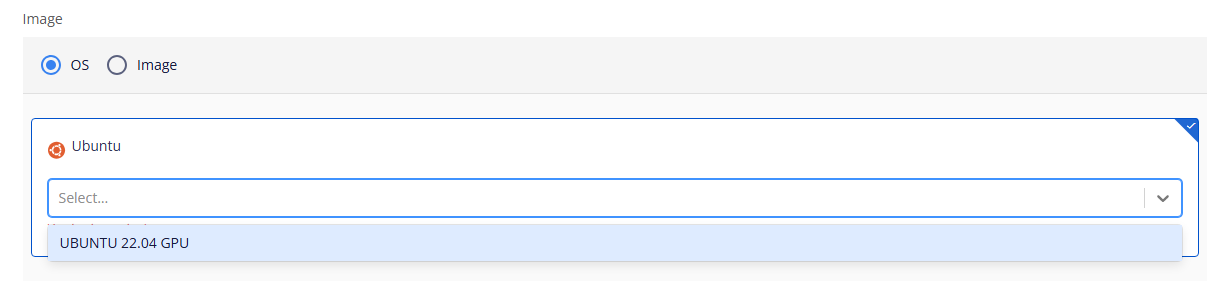
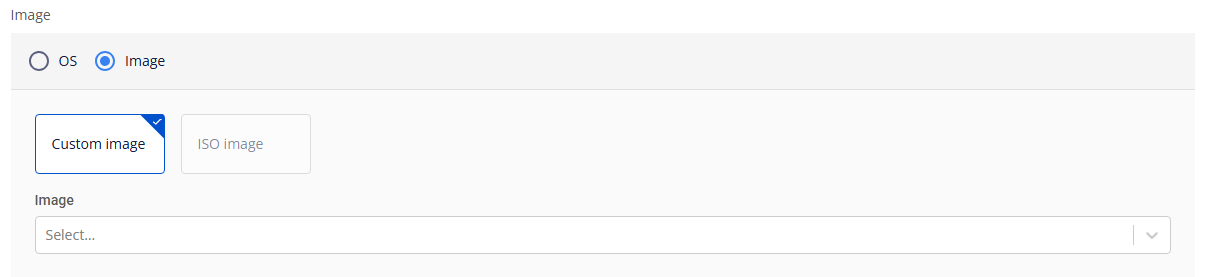
Image: You can use either the default Ubuntu base image or your own custom image.
- OS: Currently supports Ubuntu 22.04 GPU.
- Custom image: Upload your image under Custom Images (file type: QCOW). It will then appear in the image selection list.
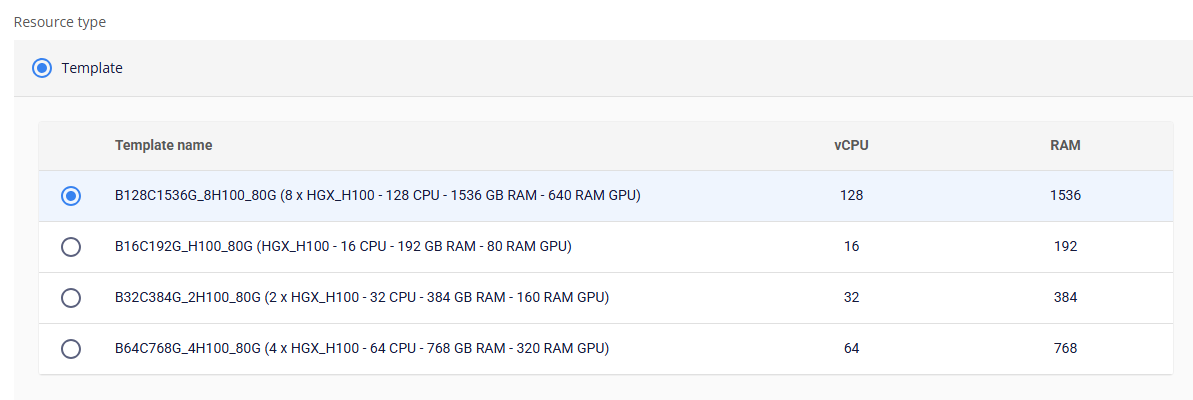
- Resource Type: Each GPU VM offers different configurations for vCPU, RAM, and the number of GPUs attached. You can choose the configuration that best fits your workload requirements.
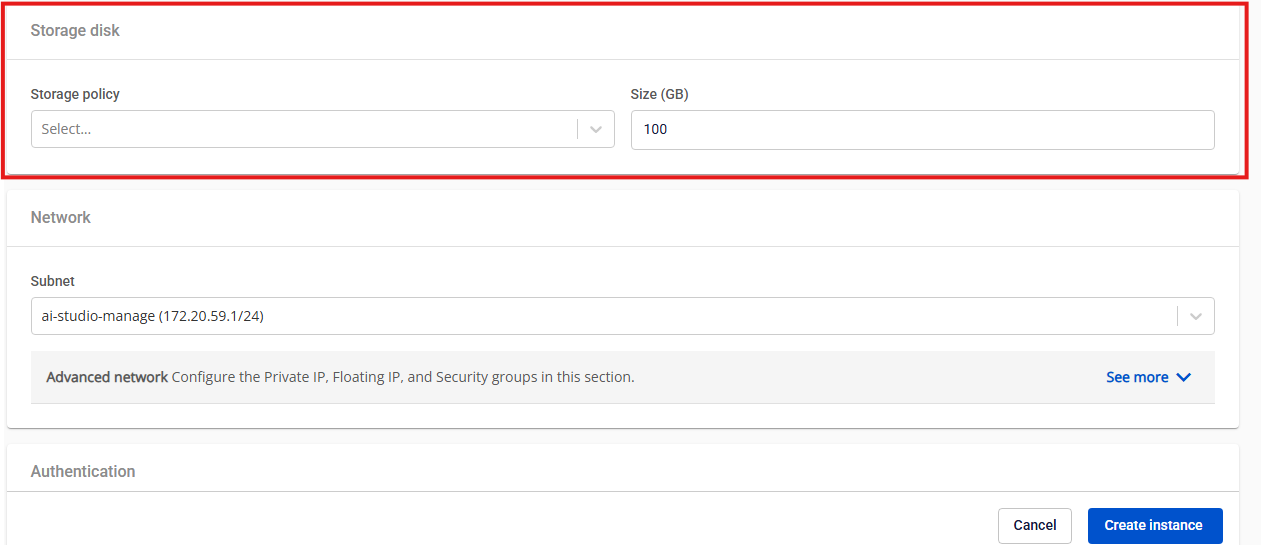
Step 3: Configure the Storage Disk
-
Storage Policy: Specifies the storage type used for the GPU VM.
-
GPU VMs with Ephemeral Disk (NVMe) support only NVMe-SSD.
-
GPU VMs with Persistent Disk support only Premium SSD, offering IOPS between 3,000 and 10,000 (depending on your service quota request).
-
-
Size:
-
Ephemeral Disk (NVMe): Fixed capacity per GPU instance (depends on the number of GPUs selected).
-
Persistent Disk: Scalable based on your storage requirements, starting from 100GB.
-
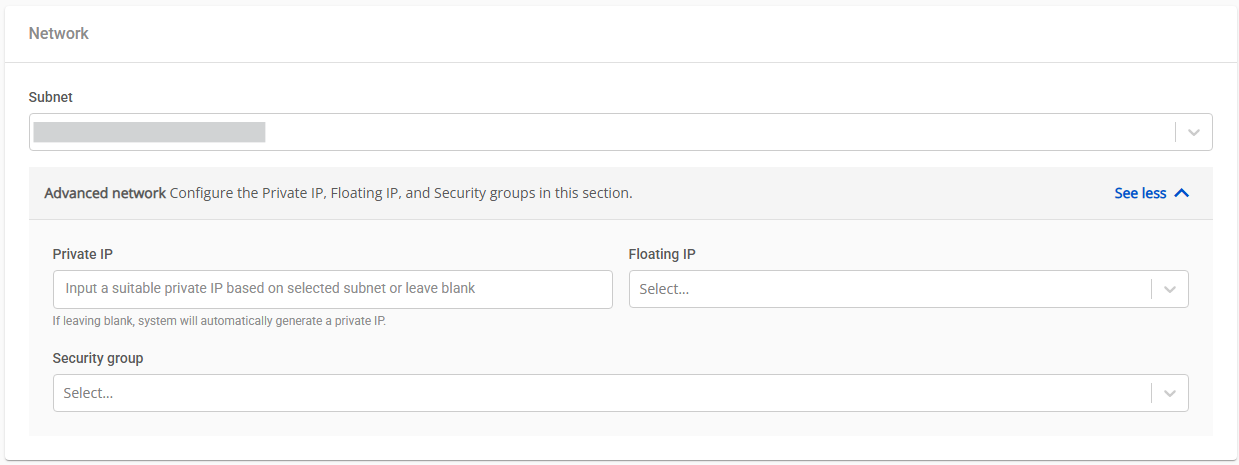
Step 4: Configure the Network Settings
-
Subnet: Select the appropriate subnet to enable your VM to connect to internal and external resources.
-
Advanced Network:
-
Private IP: Enter a private IP manually or let the system automatically assign one based on the selected subnet.
-
Floating IP: For Ephemeral Disk NVMe, the Floating IP is only configured after the VM is successfully created.
-
Security Group: Assign a security group to manage inbound and outbound traffic for the VM.
-
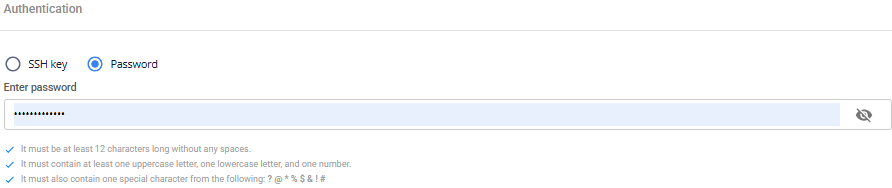
Step 5: Set Authentication Method
Choose one of the following authentication methods:
-
SSH Key: The system automatically uses your latest SSH key (you can change it if needed).
-
Password: Set a password and securely store it for console access.
Step 6: Advanced Settings
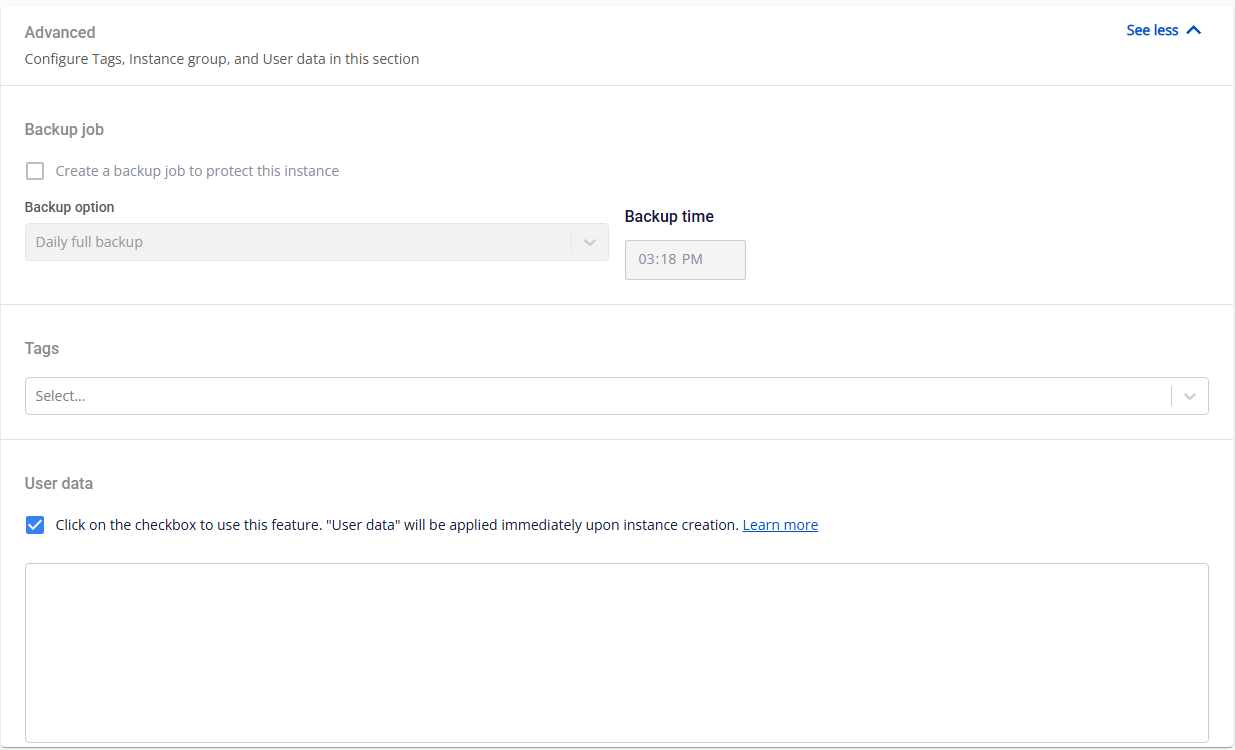
Backup Job
Only available for GPU VMs using Block Storage - Persistent Disk. You can schedule automatic backups and define their frequency and timing.
Backup Options:
-
Daily Full Backup: Performs a full backup every day.
-
Daily Incremental, Weekly Active Full: Performs daily incremental backups with a full backup once per week.
-
Daily Incremental, Monthly Active Full: Performs daily incremental backups with a full backup once per month.
Backup Time: Set the specific time for the backup to run.
Tags
Assign existing tags to help manage and categorize your resources.
User Data (Cloud-init Script)
The User Data field allows you to add cloud-init scripts.
When the VM starts, cloud-init reads metadata and automatically configures the system — including users, SSH keys, and network settings.
Sample Cloud-init Script: With the provided script, the system will automatically create the user "testcloudinit" with password "Abc123" . Another user, "testcloudinit2", with be created with the password "P@ssw0rd!"
# cloud-config
users:
- name: testcloudinit
sudo: ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
lock_passwd: false
shell: /bin/bash
passwd: $6$rounds=4096$V6anciWl30$xKbcljqks1gUkMiM80pyKzhvyhn7U1n.jXcGCUfkUlX.rnllUWKUrmDEzekhhhP8aERSylRuC7gfDhJ32Xv0A1
- name: testcloudinit2
groups: sudo
lock_passwd: false
shell: /bin/bash
plain_text_passwd: P@ssw0rd!
- hostname: testcloudinitStep 7: Create the Instance
Click Create Instance to deploy and start your GPU VM.
Once the instance is successfully created, you can view its details in the Instance Management dashboard.