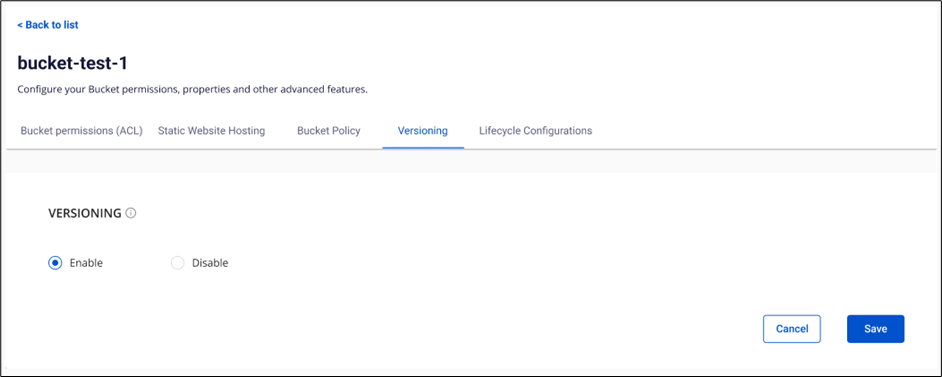
Versioning
Versioning is a feature that allows you to store and manage multiple versions of an object on FPT Object Storage. When versioning is enabled, a new version is created and stored every time you act (update or delete) on an object. You can use this feature to store and restore all versions of objects within a bucket.
Currently, FPT Portal does not allow the management of non-current versions. You can use SDK or clients to utilize this feature entirely.
To enable this feature for a bucket, follow these steps:
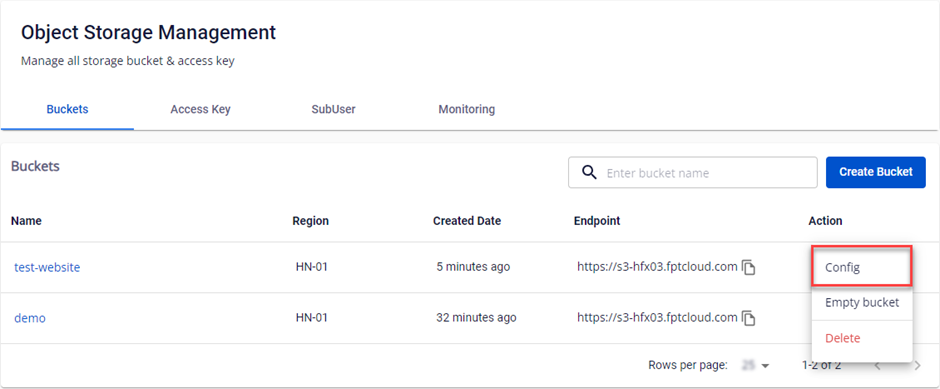
- In the Action section of the bucket you want to configure, select Config.
- Open the Versioning tab.
- Choose Enable or Disable, and click Save.
Static Website Hosting
Static Website Hosting is a feature that allows you to store the entire resources of a static website on FPT Object Storage. Instead of just storing regular files, you can use a bucket to store HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files, along with other static assets, and serve it as a website to users.
When you activate the Static Website Hosting feature for a bucket, FPT Object Storage provides you with a public URL. You can use this URL to access and share your website with users, similar to a web hosting service.
To create and configure Static Website Hosting in FPT Object Storage, follow these steps:
- Upload the entire website source to the S3 bucket.
- In the Action section of the bucket you want to configure, select Config.
- Open the Static Website Hosting tab.
- Choose ENABLE WEBSITE HOSTING and fill in the necessary information:
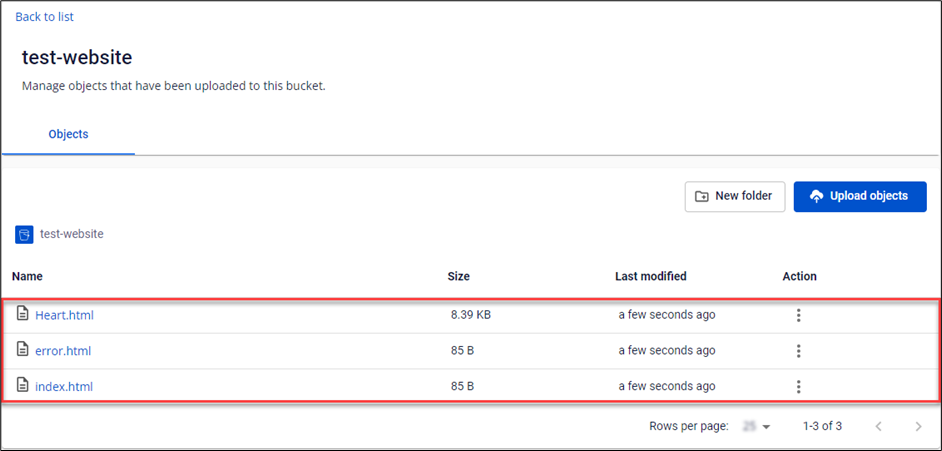
- Index Document: The homepage of the website.
- Error Document: The 404 page will be displayed if a user requests an invalid URL.
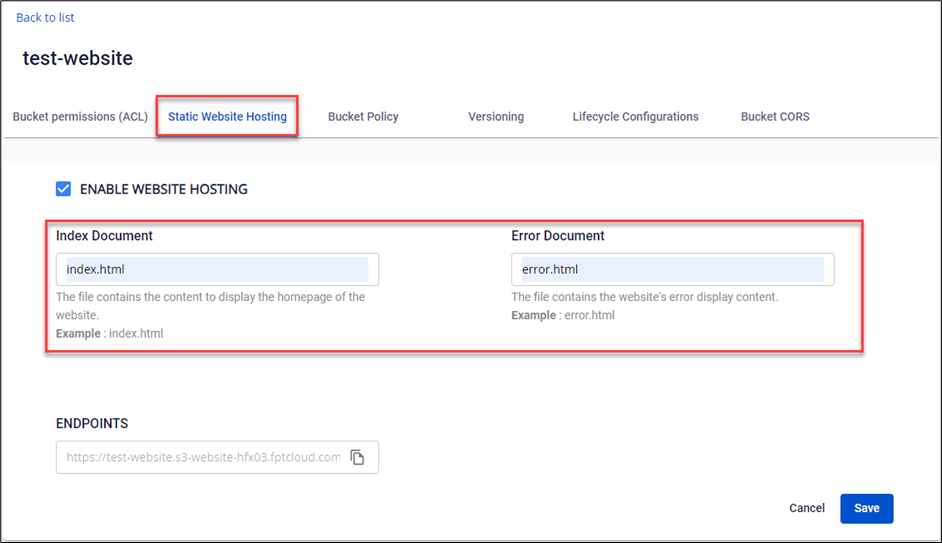
Access via Endpoints. To be accessible, files in the bucket must be in a Public state.
Lifecycle Configurations
Lifecycle Configurations is a feature that allows you to manage the objects' lifecycle within a bucket automatically. This feature is most effective for automatically deleting objects after a certain period.
You can create multiple Lifecycle Rules for a bucket, where each rule applies to a group of objects, or use a single rule for the entire bucket. A typical Lifecycle Rule consists of the following components:
- Scope: Scope determines which objects the rule will apply to. You can use it for the entire bucket or specify a prefix to apply it to a specific group of objects.
- Delete current versions of objects: Specifies when recent versions of objects within the scope will be deleted. If you are not using versioning, deleting current versions will permanently delete the object.
- Permanently delete non-current versions of objects: Specifies when non-current versions of objects within the scope will be deleted. Non-current versions are only created when using versioning, so you don't need to worry about this if you're not using versioning.
- Delete incomplete multipart uploads: Specifies when to delete incomplete multipart uploads.
- Delete expired object delete markers: Deletes expired delete markers (when there are no older versions of an object).
With Lifecycle Configurations, you can automatically manage the objects' lifecycle in a bucket, helping you save storage costs and efficiently organize data management.
Some high-risk actions have been removed from the FPT Portal, such as Permanently delete file on a particular date, Transitions Class,... If you still need these actions, use S3 Clients to configure them.
A. Create a New Lifecycle Rule
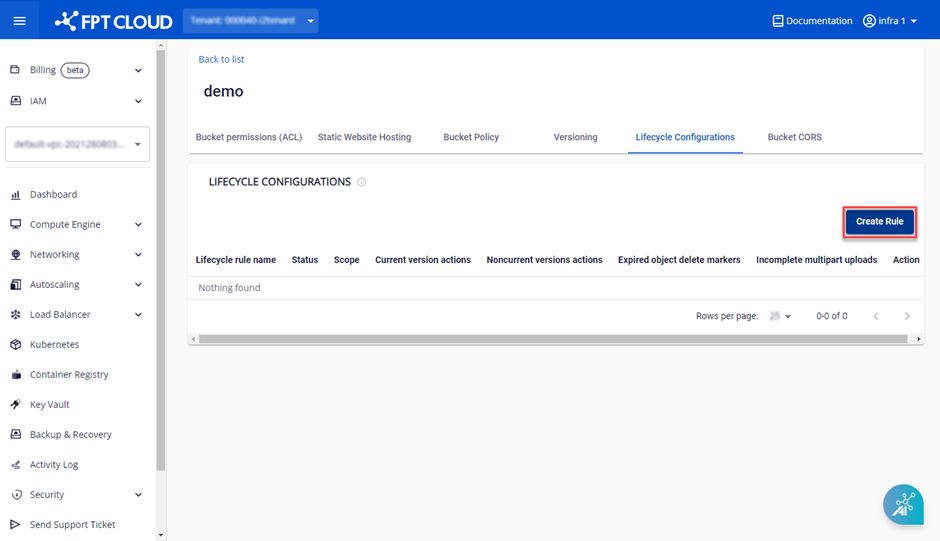
- In the Object Storage Management dashboard, select Config for the bucket you want to configure a Lifecycle Rule for.
- Open the Lifecycle Configurations tab, and choose Create Rule.
-
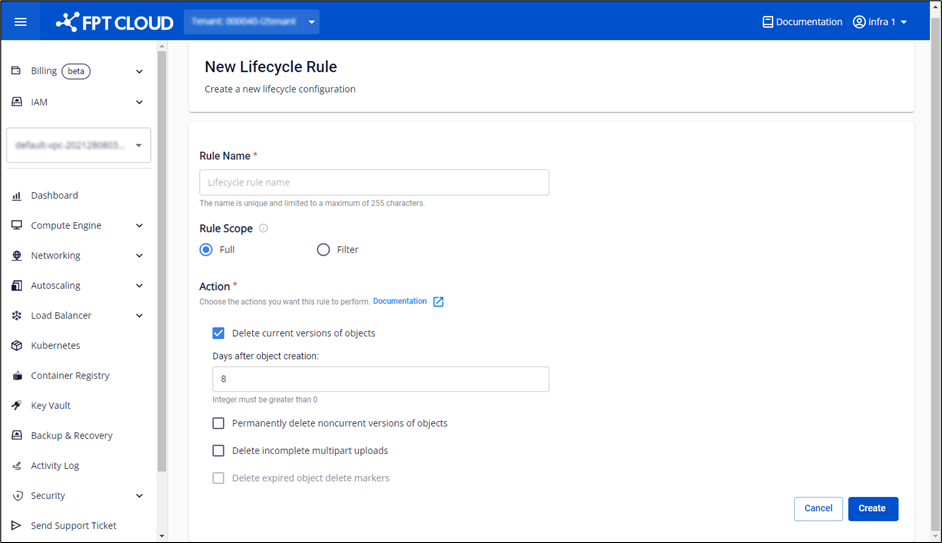
Enter the information for the Lifecycle Rule in the corresponding fields:
- Rule Name: Name of the Rule.
- Rule Scope: The scope of objects to which the rule will apply. You can apply the rule to the entire bucket (Full) or specify a prefix to apply it to a specific group of objects within the bucket.
Action Description Delete current versions of objects Select the number of days after which current versions of objects will be deleted. Permanently delete non-current versions of objects Select the number of days after which non-current versions of objects will be deleted. Delete incomplete multipart uploads Select the days after which incomplete multipart uploads will be deleted. Delete expired object delete markers Select the days after which expired object delete markers will be deleted.
- In FPT Object Storage, if you have enabled versioning, the system creates a delete marker when an object is deleted instead of immediately removing it. A delete marker is a unique entity created to indicate that the object has been deleted. Creating a delete marker helps track the deletion history and recover data in the future if needed.
- Delete markers become Expired delete markers when all older versions of the object have been deleted, leaving only one delete feature in the version list.
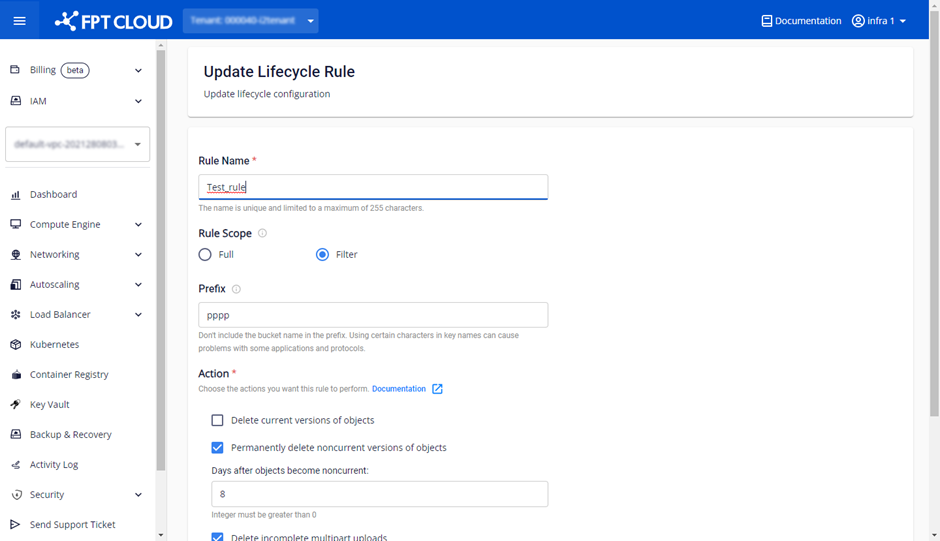
B. Update a Lifecycle Rule
- For the Lifecycle Rule you want to update, select Edit.
- Enter the updated information for the Lifecycle Rule.
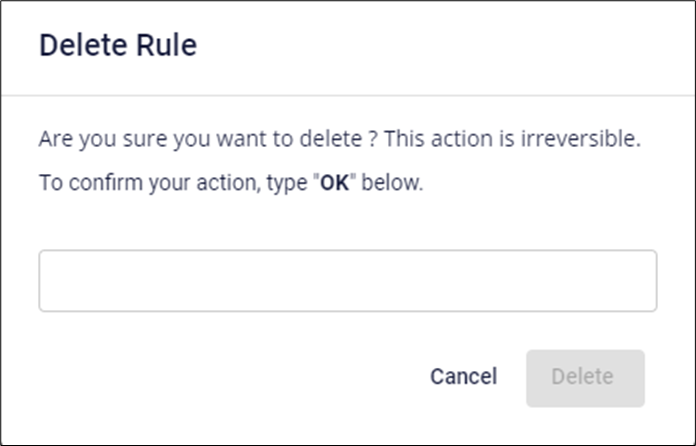
C. Delete a Lifecycle Rule
- For the Lifecycle Rule you want to delete, select Delete.
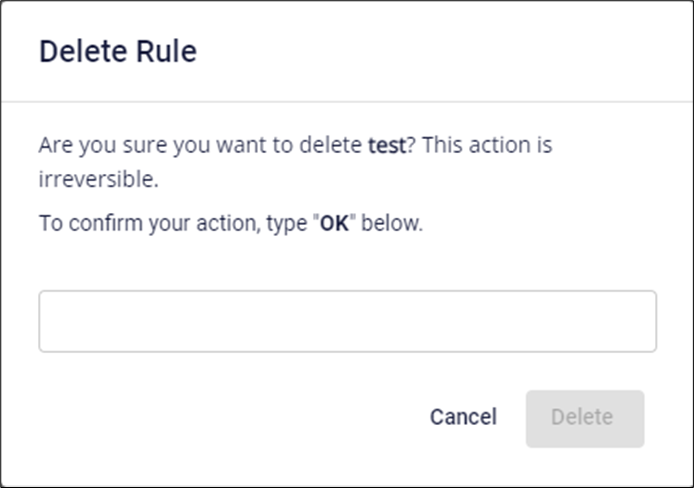
- A confirmation dialog will appear, displaying the rule name and requesting user confirmation. Select Delete to proceed with deletion.
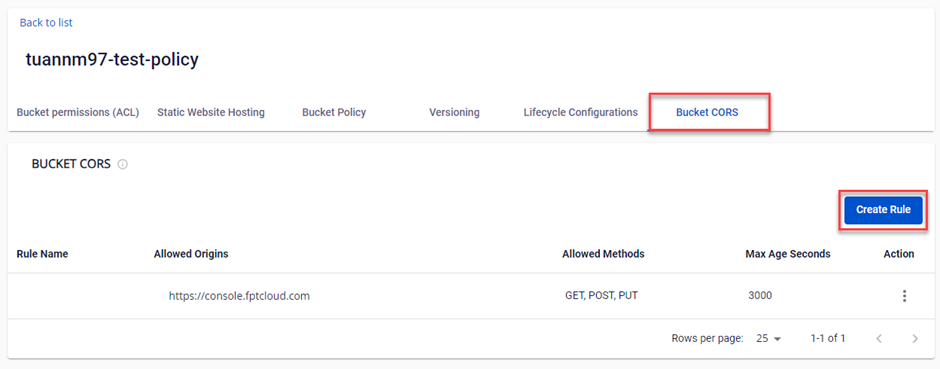
Bucket CORS Configuration
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) allows websites to interact with each other and share data securely.
By default, FPT Object Storage blocks requests from all origins (websites, servers) to the bucket. The Bucket CORS feature allows a website from a specific origin to request resources from the bucket without being blocked by the Same-Origin Policy (SOP).
When a website attempts to access resources from FPT Object Storage, the browser sends a Cross-Origin request (CORS request) to the FPT Object Storage server. The server must respond to this request with access-related information by sending HTTP headers containing CORS policies. The browser then checks these headers to determine if the access is permitted.
To allow an origin (website, server) to GET data from the bucket, you must declare them in the Bucket CORS Config.
A. Create a New Bucket CORS Rule
Step 1: In the Object Storage Management dashboard, select Config for the bucket you want to configure CORS for.
Step 2: Open the Bucket CORS tab and select Create Rule.
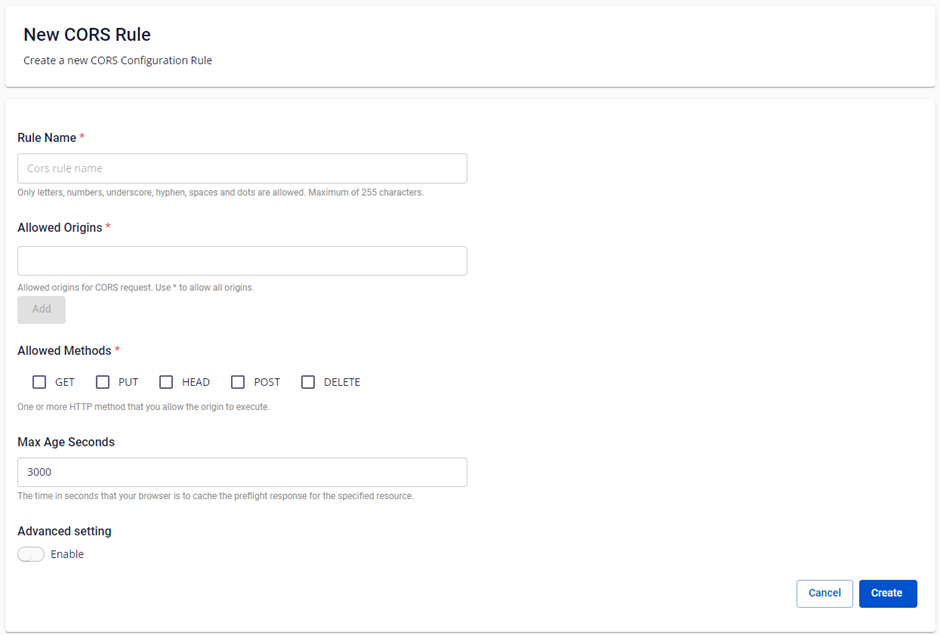
Step 3: Enter information for the CORS Rule in the respective fields:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Rule Name | Name of the Rule |
| Allowed Origins | Origins permitted for CORS requests. Use * to allow all Origins. |
| Allowed Methods | You allow Origins to execute one or more HTTP methods. |
| Max Age Seconds | Cache duration. |
| Advanced setting | Expose Headers: You want clients to access one or more response headers from their applications. Allowed Headers: Headers specified in Access-Control-Request-Headers. |
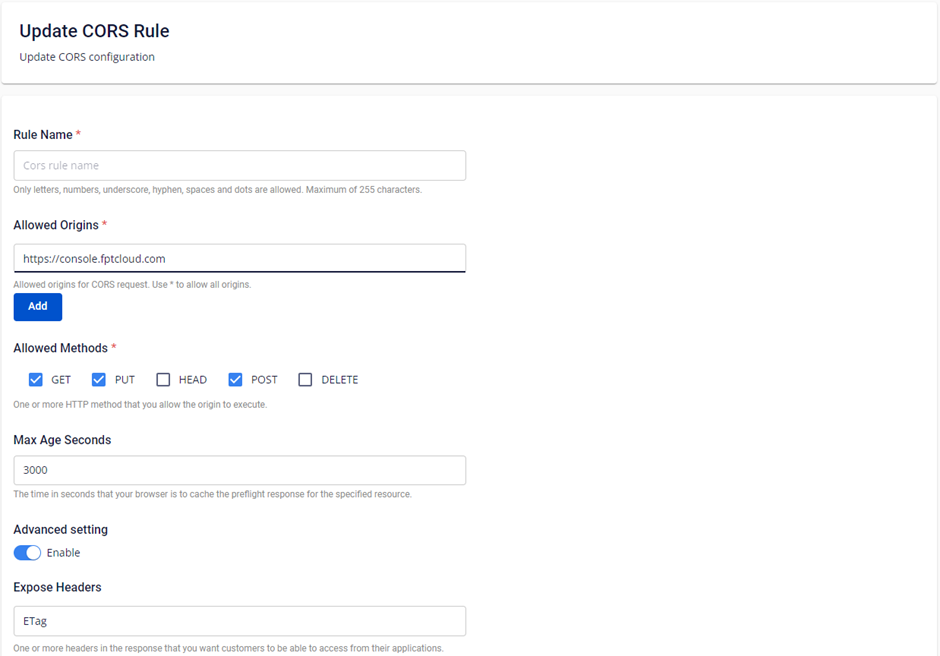
B. Update Bucket CORS Rule
Step 1: Select Edit for the Bucket CORS Rule you want to update.
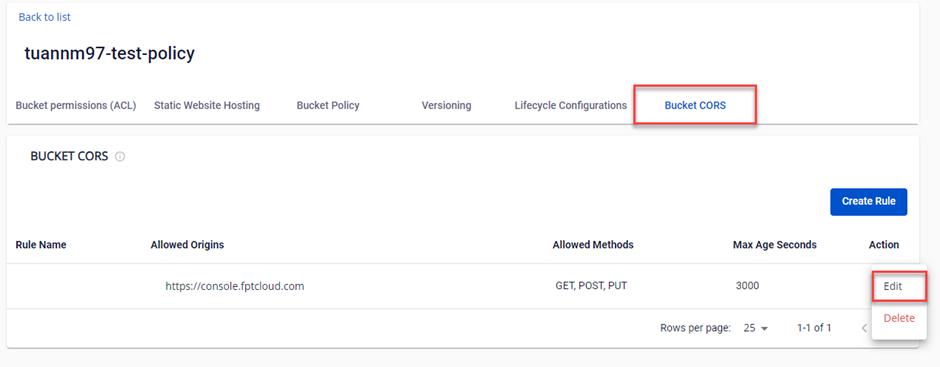
Step 2: Enter the updated information for the CORS Rule.
C. Delete Bucket CORS Rule
Step 1: Select Delete for the Bucket CORS Rule you want to delete.
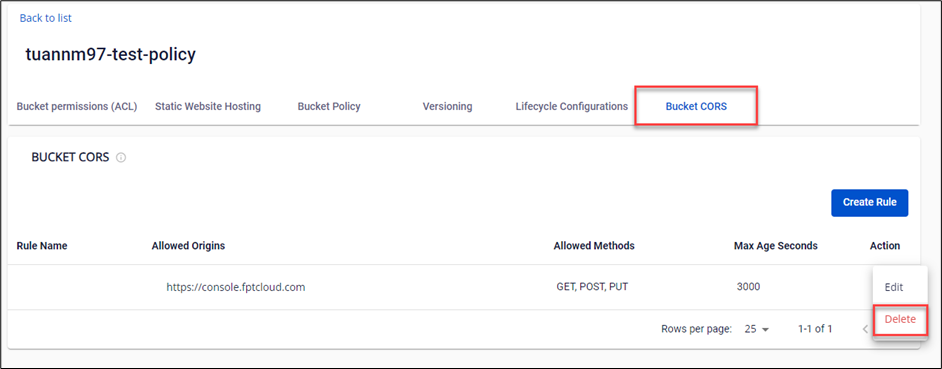
Step 2: A confirmation dialog will appear, displaying the rule's name and asking for user confirmation. Select Delete to proceed with the deletion.