Managed – FPT Database Engine
-
 Glossary
Glossary
-
 Concepts
Concepts
-
 Initial Setup
Initial Setup
-
 Tutorials
Tutorials
-
 Peformance & Benchmark
Peformance & Benchmark
-
 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
-
 FAQs
FAQs
-
The Database Engine Operations guide explains how to manage database clusters on FPT Cloud Portal. You can perform start, stop, restart, and delete actions according to cluster lifecycle states.
Operational actions
- Start: Starts a database cluster that is in the Stopped state. The cluster status changes to “Starting”, and then to “Running” when it becomes available.
- Stop: Stops a database cluster that is in the Running state. When stopped, the cluster temporarily suspends workload processing. The status changes to “Stopping” and then to “Stopped”. In this state, the database does not serve requests but can be started again when needed.
- Restart: Restarts a running database cluster. This operation stops and then starts the cluster, and is typically used to apply configuration changes or resolve transient issues. The status shows “Restarting” and returns to “Running” when the operation completes.
- Delete: Deletes a database cluster and all associated data. This action is irreversible. Once completed, the cluster is removed from the list and all related resources are released.
Action availability by database status
| Status | Meaning | Actions Available |
|---|---|---|
| Running | The database is provisioning. | Delete |
| Running | The database is operating normally. | Stop, Restart, Delete |
| Stopped | The database is stopped. | Start, Delete |
| Warning | The database is experiencing degraded performance or stability. | Delete |
| Failed | The database encountered an unknown error. If the database is no longer needed, delete it to clean up resources, or contact FPT Support for assistance. | Delete |
Perform an operation
To perform operational actions, open the Database list page, then select the “⋯” (More actions) icon in the “Action” column for the target database. The list of available actions is displayed:
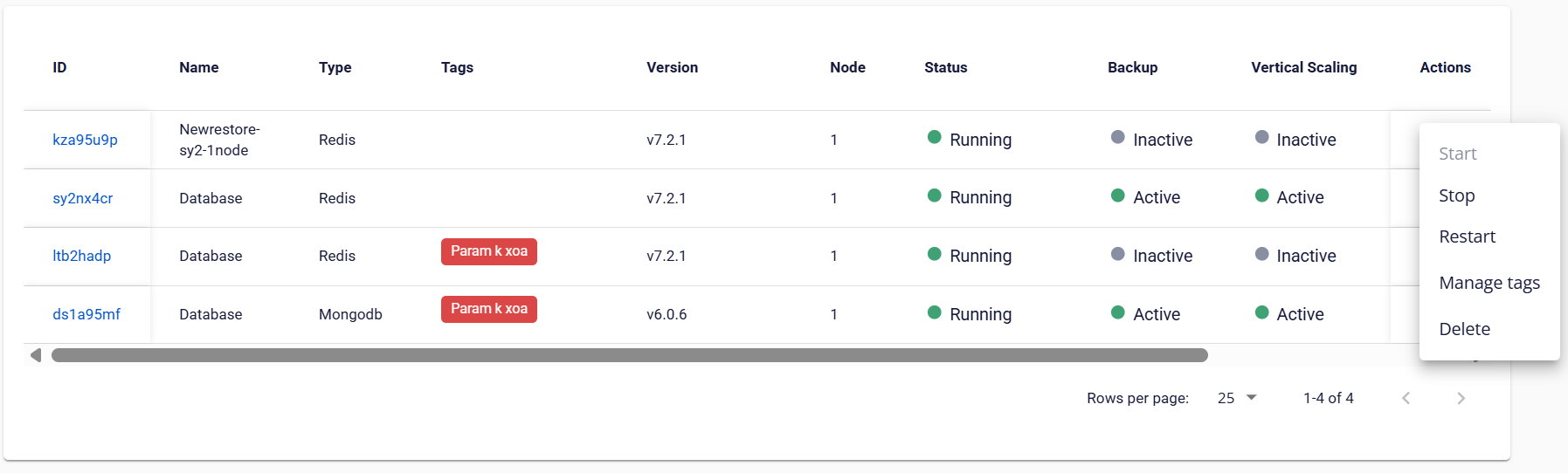
When you select an action, a confirmation dialog appears. You must explicitly confirm the action to proceed, to prevent unintended changes, especially for irreversible operations.
After confirmation, the system performs the action, which typically takes 5–7 minutes. During this time, additional operations on the database are temporarily disabled until the process completes.








