Managed – FPT Database Engine
-
 Glossary
Glossary
-
 Concepts
Concepts
-
 Initial Setup
Initial Setup
-
 Tutorials
Tutorials
-
 Peformance & Benchmark
Peformance & Benchmark
-
 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
-
 FAQs
FAQs
-
The Restore and Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) features allow users to recover a database from existing backups or restore a database to a specific point in time in the past. This section provides detailed instructions to help users perform data recovery accurately, safely, and efficiently, while ensuring data integrity.
When performing Restore or PITR, the system will create a new database cluster and will not overwrite the existing cluster.
Currently, FPT Cloud supports Restore for all available database engines and supports PITR for PostgreSQL.
1. Restore database
The Restore feature allows users to use a previously created backup to recover data and create a new database cluster. This is useful in cases of data loss, system failures, or when a rollback to a previous state is required.
Before performing a restore, ensure the database cluster has at least one successfully created backup (restore point) - meaning at least one restore point is available.
Steps to perform restore:
Step 1: Access the Restore screen
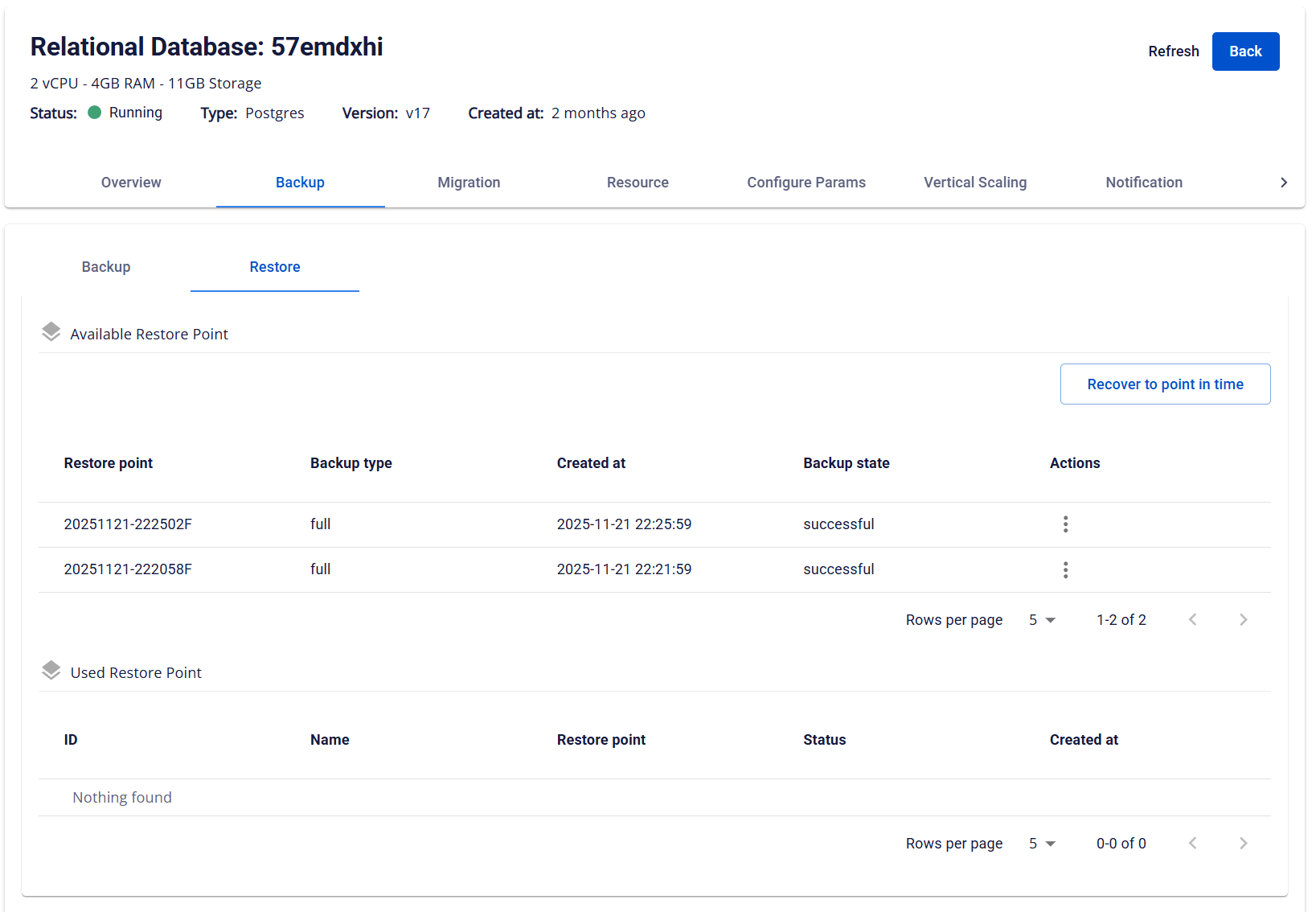
From the menu, select Database Platform → choose All Database or the relevant database group → click the Cluster ID of the database cluster to restore → select the Backup tab → choose the Restore sub-tab. The system displays a list of Available Restore Points, including backup types (Full or Diff):
Step 2: Perform restore
In the Actions column, click the ellipsis icon (⋮) corresponding to the desired restore point > select Restore. The Restore Database dialog appears:
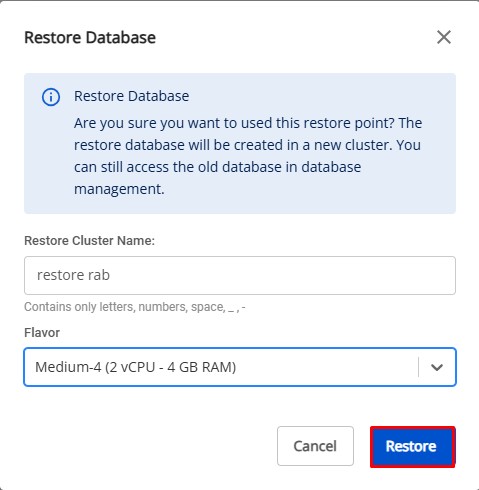
Enter the required information:
- Restore Cluster Name: Enter a name for the restored cluster.
- Flavor: Select an appropriate configuration for the restored cluster.
Click Restore to start the recovery process. Upon successful restore, a new database cluster will appear in the Database Engines list containing data from the selected backup.
2. Recover to Point-in-Time
The Recover to Point-in-Time feature allows users to restore a database to an exact point in the past, which is especially useful when recovering from incidents or operational errors.
Currently, this feature is supported only for PostgreSQL.
Before performing PITR, ensure that:
- PITR is enabled for the database cluster.
- At least one full backup exists
- Required archived logs are available for recovery.
Steps to Perform Recover to Point-in-Time:
Step 1: Access the Restore screen
Follow the same steps as accessing the Restore screen in the Restore Database section.
Step 2: Perform recover
On the Restore tab, click the Restore to point in time button > The Restore Database to a Point in Time popup appears:
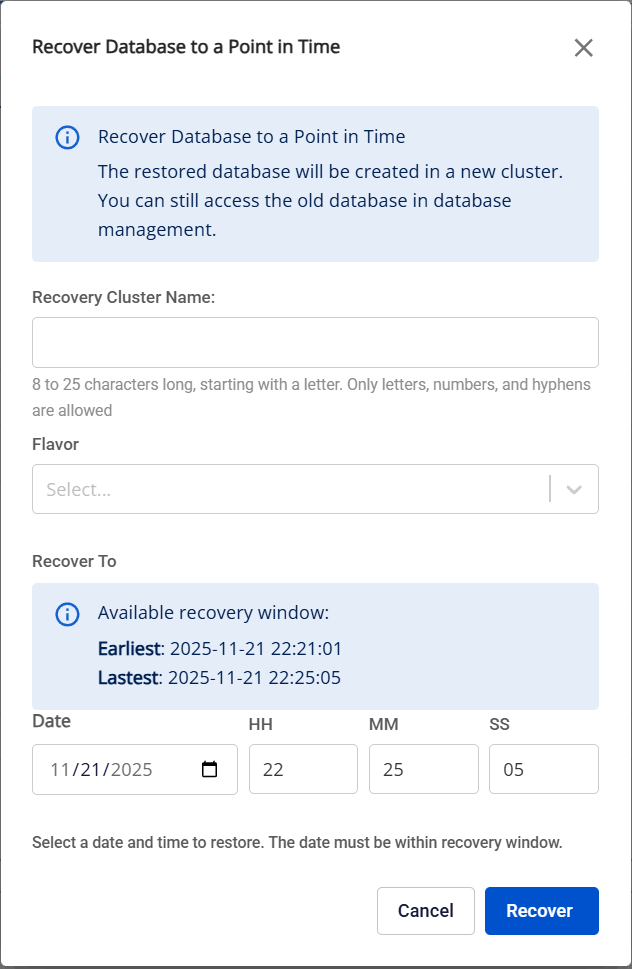
Enter the required information:
- Restore Cluster Name: Enter a name for the restored cluster.
- Flavor: Select an appropriate configuration for the restored cluster.
- Recover To: Select the exact time to which you want to restore the database (in date-time format).
Click Recover to start the recovery process. The system will create a new cluster and restore data to the specified point in time. Upon successful recovery, a new cluster will appear in the Database Engines list screen containing data at the recovery time.
Note: You can only recover data to points in time after the first Full Backup has been created since PITR was enabled. If this Full Backup has not yet been executed, the PITR feature will not be available. Any data changes that occurred before this Full Backup point are not protected by PITR and cannot be recovered.








